Load Handling

When it comes to picking up, securing and transporting loads, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) require a wide range of information to ensure safe and smooth processes. First, the automated vehicle must dock precisely at the correct transfer station. During loading and unloading, it must be ensured that the load carriers are reliably detected and correctly positioned. Load identification can also become a challenge if, for example, several objects are to be detected simultaneously or a robot mounted on the AGV has to be controlled accurately.
From docking to load detection and positioning to load identification, Pepperl+Fuchs offers an extensive portfolio of compact and robust sensors that are ideal for use in automated guided vehicles. For example, noncontact technologies ensure safe material transfer, while powerful identification systems reliably identify the load carriers even under harsh conditions.
Discover our load handling solutions for your AGV in an interactive way!
Solutions for Docking

For correct transfer of goods, automated guided vehicles must automatically find the correct position at the transfer station. Since the subsequent steps are often safety-relevant, the requirements of functional safety must be met at this point. This is ensured by the safePGV positioning system, which enables safe positioning and identification up to SIL 3/PL e with a single sensor.

During loading and unloading, mobile robots must dock correctly at a station to guarantee smooth transfer of the load carrier. Simple but robust signal transmission is required to control this process. With two thru-beam photoelectric sensors of type BB10, this task can be solved in a space-saving and cost-effective way. Two different transmission frequencies ensure interference-free signal transmission—even with surrounding metal structures.

During the transfer of load carriers, hazardous movements can occur at the docking station. To ensure both the safety of the operating personnel and consistent system availability, DAD15 optical data couplers are used. This robust, cost-effective solution provides safety verification of the correct vehicle position up to PL d.
Solutions for Load Positioning and Detection
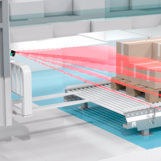
When loading and unloading automated guided vehicles at transfer stations, the position of the load must be precisely detected. To ensure correct transfer, an R2300 3-D LiDAR sensor is mounted on the vehicle's mast. This provides measurement data as the AGV approaches and as the load is loaded, which is available to the control system as a 3-D point cloud.

When transporting goods, pallets are picked up by automated guided vehicles, brought to their destination and set down again there. To ensure that the pallets are not displaced in the process, the SmartRunner Explorer 3-D vision sensor mounted on the vehicle provides a high-resolution 3-D image of the target object as the data basis for vehicle control.

AGVs frequently transport components that are located in trolleys. To prevent these carts from tipping or rolling away during travel, they must be positioned correctly on the vehicle. Inductive safety sensors ensure reliable detection of the material cart position up to SIL 2/PL d. With their compact design, they can be easily integrated into automated guided vehicles.

In production halls and warehouses, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) often transport goods placed on Euro pallets. The OQT400-R200 triangulation sensor is used for error-free detection of pallet feet. Due to multipixel technology (MPT), this sensor is particularly insensitive to the effects of ambient light and reliably suppresses undefined background reflections. In this way, pallet feet are detected accurately at all times and false detections are suppressed.

For forklift AGVs to be able to pick up or set down pallets, the forks must be moved precisely to the target position—in high-bay warehouses even over large differences in height. The ECA10TL cable-pull rotary encoder detects the height position of the fork with maximum precision. The robust design of the rotary encoder and measuring cable enables use in harsh environmental conditions—whether dust or dirt, moisture, or severe temperature fluctuations.
Solutions for Load Identification

RFID systems are the ideal choice for reliable identification of loads independent of environmental influences. Since automated guided vehicles often operate under harsh conditions, the RFID systems used must be able to withstand large thermal and mechanical loads. The ultra-rugged F61 RFID read/write device is perfect for this task. Its compact design makes it particularly easy to integrate into automated bots.

If there are various objects on a load carrier, it is difficult to correctly identify the products belonging to a transport order. The F190 RFID read/write device is designed to meet this challenge. It detects up to 40 tags in a single read operation using multitag detection. Due to the high transmission power of the read device, the RFID tags can be detected as soon as the vehicle approaches the load carrier, so there is no loading delay.

When transporting trolleys or racks, automated bots drive into a recess under the load carrier to lift it. Here, the PGV positioning system performs two tasks in one: A PGV read device mounted on the top of the vehicle identifies the load carrier with the aid of a Data Matrix tag. At the same time, the relative position of the vehicle is determined based on the orientation of the read device to the tag. This ensures precise alignment of the AGV and safe transport of the load carrier.

AGVs on which a collaborative robot with multi-axis arm is mounted are being used more and more frequently in production to feed the required components to the machines. The controller requires a variety of different information to reliably detect the objects and accurately determine the positions to be approached. For this application, the 2-D universal vision sensor VOS2000 offers a flexibly combinable vision tool set, including for position and shape detection, matching, and identification tasks.






 +47 3557 3800
+47 3557 3800